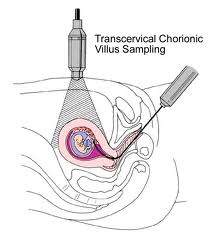
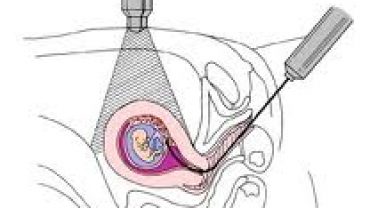
 Chorionic villus sampling is usually done early in pregnancy between the 9th and 13th week. This is a procedure that involves removing a sample of chorionic villi cells from the placenta at the point where it attaches to the uterine wall.
Chorionic villus sampling is usually done early in pregnancy between the 9th and 13th week. This is a procedure that involves removing a sample of chorionic villi cells from the placenta at the point where it attaches to the uterine wall.
In the more common trans-cervical method, ultrasound is used to guide a thin catheter through your cervix to the placenta. A small amount of chorionic villi cells are gently suctioned into the catheter. The trans-abdominal method is similar to amniocentesis and depends on ultrasound guidance. A long, thin needle is inserted through your abdomen into the placenta, where a small sample is withdrawn.
CVS is done for many reasons, but the main reason is for early detection of chromosome abnormalities, such as Down syndrome and other genetic disorders. CVS cannot diagnose neural tube defects because it doesn’t sample any amniotic fluid for testing levels of AFP.
The risk of a pregnancy ending in miscarriage are higher with CVS (one in 100) than with amniocentesis. Recent studies suggesting an association between CVS and limb malformation have made some doctors hesitant to offer this procedure.
Since CVS provides a larger sample of cells than amniocentesis, results take a little less time to obtain. Some results may be possible within a day or two.
More Prenatal Tests
—Amniocentesis
—Contraction Stress test (CST)
—Glucose Tolerance Testing
—Hemoglobin Test
—MSAFPT Test
—Non-Stress (NST) Test
—Rh Factor
—Triple Screen Test
—Ultrasound
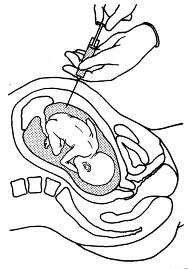 The amniocentesis test is a test in which a needle is used to remove a sample of fluid from the amniotic sac surrounding your baby. The amniotic fluid, which contains cell shed by your baby, is then studied in a lab for analysis. If done for chromosome analysis, amniocentesis is usually performed after the 16th week of pregnancy. If a woman needs to give birth early for some medical reason, amniocentesis might be done shortly before delivery to asses fetal lung maturity.
The amniocentesis test is a test in which a needle is used to remove a sample of fluid from the amniotic sac surrounding your baby. The amniotic fluid, which contains cell shed by your baby, is then studied in a lab for analysis. If done for chromosome analysis, amniocentesis is usually performed after the 16th week of pregnancy. If a woman needs to give birth early for some medical reason, amniocentesis might be done shortly before delivery to asses fetal lung maturity.