(continued “preconception”)
These special preconception recommendations, developed through a consultation process with a select panel of specialists, include maximizing public health surveillance and monitoring which includes improving health programs and policies, the offer of pre-pregnancy checkups for women/couples who are planning a pregnancy, increasing the public’s knowledge and awareness of the importance of preconception health and encouraging everyone to have a reproductive life plan that focuses on drawing attention to reproductive health to reduce unplanned pregnancies, fetal exposure to teratogens, age-related infertility and to improve pregnancy outcomes.
Other new recommendations include augmentation of research, additional interconception (the time between pregnancies) care and intervention for women who had a previous pregnancy that resulted in infant death, preterm birth or birth defects to reduce future risks, provide preventive visits along with primary care visits for risk assessment and educational counseling related to reproductive health risks, integration of preconception health components into existing public health programs, increase the number of women who receive timely interventions following preconception risk screening and increase public as well as private health insurance coverage for low-income women to improve preventative and preconception health access and affordability.
Preconception care is a good idea, making a difference in the lives of future babies and helping them have the healthiest start possible, but will be difficult to include as part of standard medical appointments, according to some doctors. In addition, most health insurance companies don’t even have a billing code to allow doctors to begin billing for it. CDC is requesting the American Medical Association (AMA) develop a billing code for preconception care to allow doctors the opportunity of offering these additional preconception services to women. Preconception care recommendations should be implemented over a period of time within the next 2-5 years.
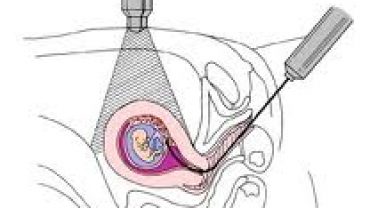
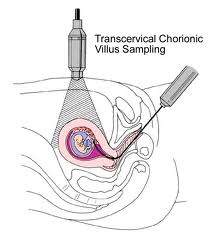 Chorionic villus sampling is usually done early in pregnancy between the 9th and 13th week. This is a procedure that involves removing a sample of chorionic villi cells from the placenta at the point where it attaches to the uterine wall.
Chorionic villus sampling is usually done early in pregnancy between the 9th and 13th week. This is a procedure that involves removing a sample of chorionic villi cells from the placenta at the point where it attaches to the uterine wall.
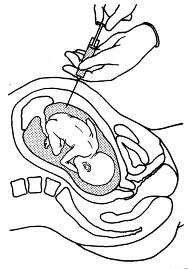 The amniocentesis test is a test in which a needle is used to remove a sample of fluid from the amniotic sac surrounding your baby. The amniotic fluid, which contains cell shed by your baby, is then studied in a lab for analysis. If done for chromosome analysis, amniocentesis is usually performed after the 16th week of pregnancy. If a woman needs to give birth early for some medical reason, amniocentesis might be done shortly before delivery to asses fetal lung maturity.
The amniocentesis test is a test in which a needle is used to remove a sample of fluid from the amniotic sac surrounding your baby. The amniotic fluid, which contains cell shed by your baby, is then studied in a lab for analysis. If done for chromosome analysis, amniocentesis is usually performed after the 16th week of pregnancy. If a woman needs to give birth early for some medical reason, amniocentesis might be done shortly before delivery to asses fetal lung maturity.